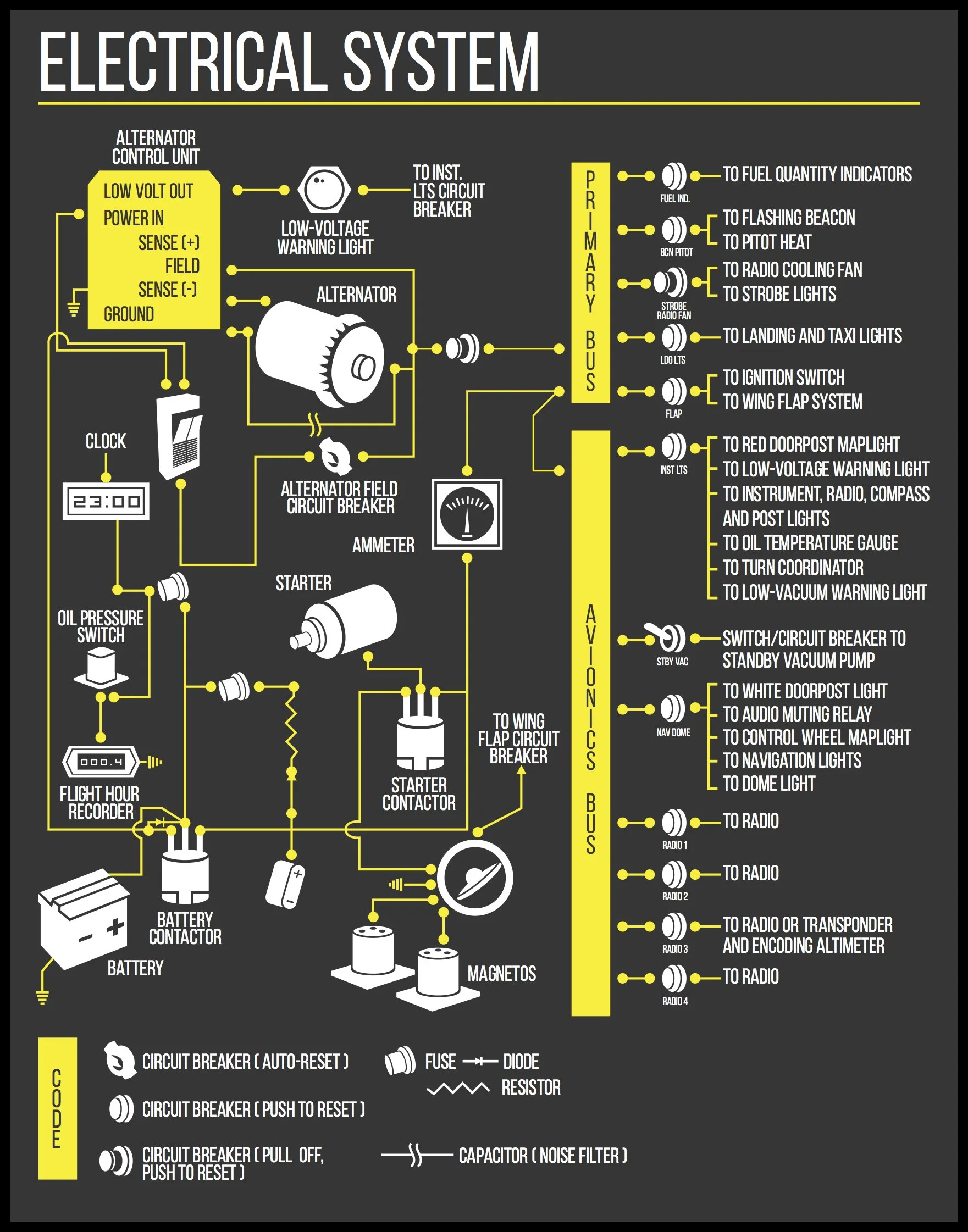
14 Or 28-Volt Direct Current (DC) Electrical System
Most airplanes manufactured after 1990 have a 28-volt electrical system that powers all of the electrical components used in flight. A 24-volt battery supplies the electrical power to start the engine. Then an engine-driven alternator or generator takes over, powering all of the electrical components in the aircraft and recharging the battery with the additional 4-volts. Some older aircraft have a 14-volt electrical system that utilizes a 12-volt battery. Both generators and alternators convert rotational energy from the engine into electricity, but generators produce direct current (DC) and alternators produce alternating current (AC). Most of the electrical equipment in aircraft utilizes direct current, so power supplied by the alternator must be converted to DC. Alternators are the norm in piston engine aircraft because they produce more power for their size and weight and also produce more power at low RPMs. Nevertheless, operations at low RPMs may not generate enough current to power all of the electrical components and the battery can become depleted.